As Malaysia accelerates its move toward digital infrastructure and data-driven decision-making, technologies like LiDAR are becoming increasingly vital. For those unfamiliar with the term, LiDAR means a method of remote sensing that uses laser light to measure distances and generate precise three-dimensional maps of the earth’s surface.
In practical terms, LiDAR allows professionals in construction, environmental monitoring, agriculture, and urban planning to collect accurate spatial data quickly and efficiently. This technology is now playing a transformative role across Malaysia, helping both public agencies and private firms plan better, build smarter, and reduce risks.
In this article, you will get to understand LiDAR meaning, usage and also challenges and limitations for LiDAR.
What is LiDAR?
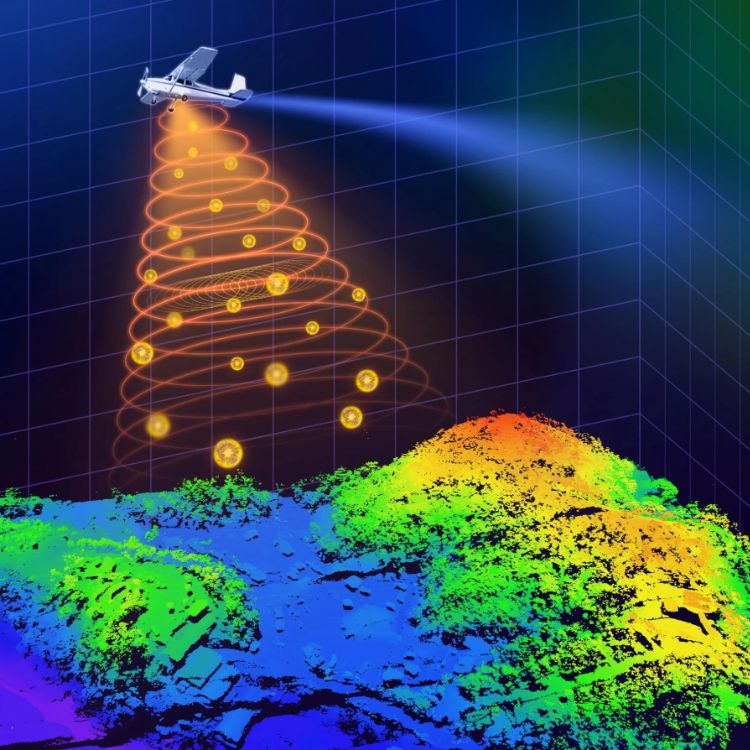
LiDAR, short for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to create highly accurate, three-dimensional maps of the Earth’s surface. It works by sending out rapid pulses of laser light and measuring how long it takes for them to bounce back. These time measurements are then converted into distance data, allowing the system to generate a detailed 3D model of the terrain, buildings, or vegetation.
In the Malaysian context, LiDAR has gained importance across multiple sectors, from mega construction projects to environmental conservation due to its ability to offer high-resolution, real-time data that supports precision planning and decision-making.
LiDAR Used in Malaysia
LiDAR technology has seen increasing adoption in Malaysia across various sectors, thanks to the government’s push towards digitalisation, smart urban development, and sustainable resource management.
Urban Development
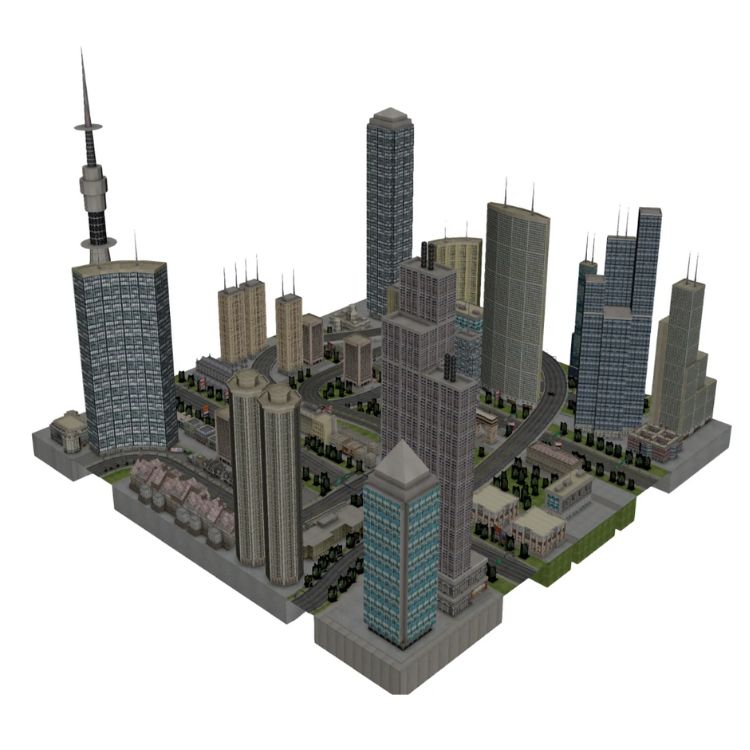
City planners and municipal councils use LiDAR for land use planning, building height analysis, and zoning control. By creating accurate 3D city models, authorities can visualise urban density, manage shadow impacts, and simulate infrastructure expansion.
Smart Cities
LiDAR plays a vital role in the Smart City Framework developed under Malaysia’s Smart City initiatives. Municipalities use LiDAR for integrating GIS data, traffic monitoring, and infrastructure health assessments.
DBKL (Dewan Bandaraya Kuala Lumpur)

DBKL uses LiDAR for drainage modelling, slope monitoring, and flood risk management in critical zones like Bukit Bintang and Jalan Tun Razak.
MBPJ (Majlis Bandaraya Petaling Jaya)
MBPJ applies LiDAR data in urban green space planning, building compliance, and transportation analysis.
MPBP (Majlis Perbandaran Batu Pahat)
In developing mixed-use zones and satellite townships, MPBP has deployed LiDAR to better manage terrain variation and water flow control.
MPK-Kluang (Majlis Perbandaran Kluang)
MPK-Kluang integrates LiDAR in waste management optimization and underground infrastructure mapping.
Forestry & Environmental Monitoring
Malaysia’s tropical rainforests are among the most biologically diverse on Earth, and LiDAR helps in canopy height measurement, biomass estimation, and deforestation tracking. Agencies like FRIM and Perhilitan use LiDAR for forest inventory and biodiversity mapping.
Infrastructure & Transportation

From expressways to rail lines, LiDAR enables precise route alignment, earthwork volume estimation, and slope stability assessment. Projects like the East Coast Rail Link (ECRL) and Pan Borneo Highway benefit from LiDAR during feasibility and construction phases.
Agriculture & Plantation Management
LiDAR is used for terrain modeling, drainage planning, and crop yield prediction in oil palm and rubber plantations. It supports plantation management in regions like Johor, Sabah, and Perak, especially in identifying flood-prone areas and improving irrigation.
Disaster Risk Management
In flood-prone states like Kelantan and Pahang, LiDAR supports hydrological modelling, floodplain mapping, and landslide risk assessments. Post-disaster analysis and recovery planning also use LiDAR data for rapid damage assessment.
LiDAR Ecosystem in Malaysia
Malaysia’s LiDAR ecosystem includes:
- Government bodies: JUPEM, PLANMalaysia, and FRIM
- Universities & R&D centres: UKM, UTM, and UM conduct LiDAR-related research and provide data processing services.
- Private sector providers: Companies such as Aerodyne Group, MSS Geoservices, and Geotechnica offer end-to-end LiDAR solutions using drones and aircraft.
- Regulators & policy makers: Agencies like PLANMalaysia are integrating LiDAR into smart city and land use policies.
The ecosystem is also supported by funding through state and federal-level development plans, ensuring LiDAR adoption continues to grow alongside national infrastructure and environmental goals.
Challenges & Limitations for LiDAR
Despite its benefits, several challenges affect LiDAR adoption in Malaysia:
- High Initial Cost: Equipment, data acquisition, and skilled manpower can be expensive.
- Weather Dependency: Cloud cover and heavy rain can interfere with data accuracy, particularly for aerial surveys.
- Data Volume: LiDAR generates massive datasets that require powerful processing tools and trained analysts.
- Limited Access to Technology in Rural Areas: Infrastructure and funding gaps make rural deployment less feasible.
However, these challenges are being progressively addressed through government support, public-private partnerships, and local R&D.
LiDAR Services by Geotechnica
At Geotechnica, we offer a suite of professional LiDAR solutions in Malaysia, backed by real-world deployments and technical precision.
Airborne LiDAR
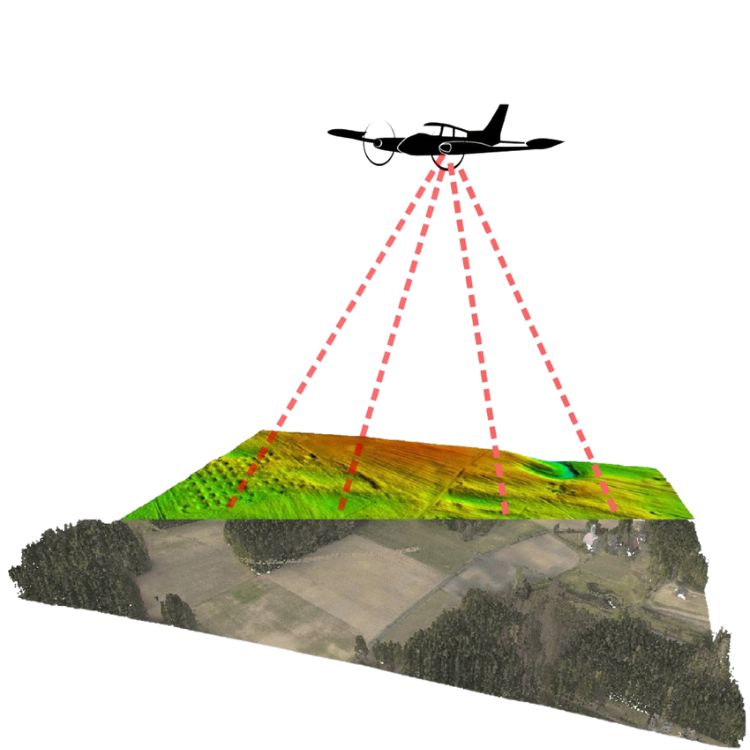
Utilizing aerial LiDAR sensors mounted on fixed-wing aircraft or helicopters, Geotechnica delivers high-resolution topographic mapping ideal for large-scale geotechnical and infrastructure projects. Applications include:
- Terrain modeling for slope stability assessments
- Flood-risk mapping across extensive catchment areas
- Digital Elevation Models (DEM/DSM) for large infrastructure layouts
These airborne systems allow rapid scan expansive, often inaccessible terrains, producing detailed 3D terrain datasets crucial for engineering planning and hazard identification.
“Airborne LiDAR systems… [are] more accurate than other remote sensing techniques; faster and cheaper data acquisition than conventional survey methods for medium – large areas; accurate measurement of ground elevation underneath dense forest canopy; no ground intrusion… robust against human error from conventional surveys.”
— Ground Data Solutions FAQ
Drone (UAV) LiDAR
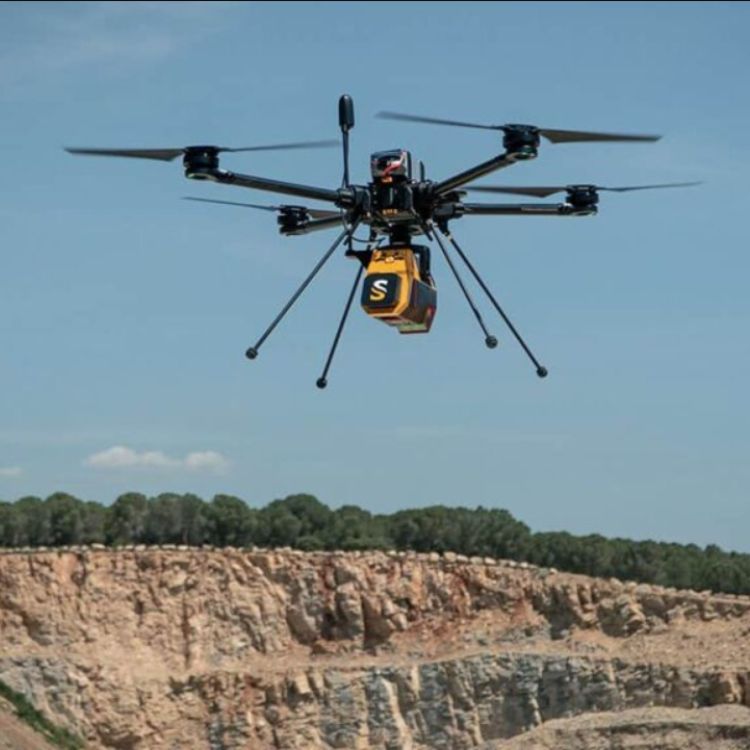

Geotechnica also employs drone-mounted LiDAR for targeted, site-specific work. Benefits include:
- Millimetre-level accuracy over small to mid-sized areas
- Safe, efficient data capture in urban zones, steep slopes, and forested sites
- Fast deployment for slope deformation monitoring, earthwork volume estimation, and vegetation clearance mapping
This approach is especially valuable for frequent revisits such as monthly slope inspections or progress checks on construction sites without disrupting ongoing operations.
Whether you’re managing a complex infrastructure project, monitoring slope stability, or conducting environmental assessments, Geotechnica’s LiDAR solutions provide the accuracy and speed you need. Get in touch with Geotechnica today to explore how our LiDAR expertise can support your project’s success. Visit Geotechnica or contact our team for a consultation today.



