GEOLOGICAL TERRAIN MAPPING REPORT (GTMR)
The compulsory procedure for future development in Malaysia


INTRODUCTION
ABOUT GTMR
Geological Terrain Mapping is the process of planning for developments and management of geohazards, basic information such as geology, topography and landform as well as information of other potentially unstable area due to the presence of landslides or severe erosion are required from an area.
Such information will assist in the preparation of layout plans, design of the infrastructure, foundation and the method of construction. This approach will minimize the risk of geohazards such as landslides or rock falls. Terrain information needed by resource managers and developers needs to be prepared according to required standards. This includes preparation of thematic maps: Slope Gradient Factor Map, Terrain Classification Factor Map, Terrain Component Attribute Factor Map and Erosion Attribute Factor Map. Digital Terrain Map (DTM) were obtained from the topographic survey and mosaic together.


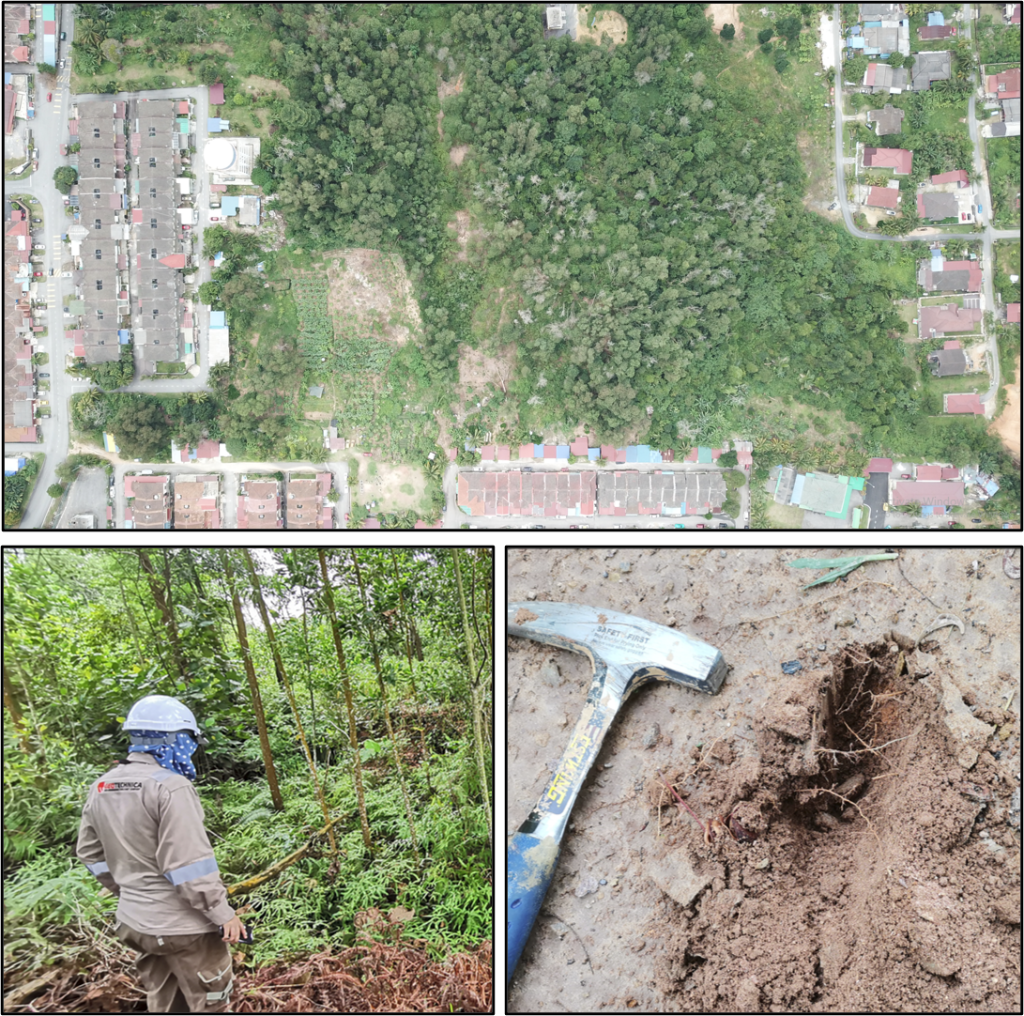
Orthophoto
An orthophoto is an aerial photograph that has been geometrically corrected or ‘orthorectified’ such that the scale of the photograph is uniform and utilized in the same manner as a map. An ortho-photograph can be used to measure true distances of features within the photograph. Planimetric corrections have been applied to remove lens distortions and optics, camera angle, and differences in elevation (topographic relief) through a process of measuring ground control points to ‘tie’ the photo to the ground. An orthophoto is an accurate representation of the Earth’ s surface. Orthophotos have the benefits of high detail, timely coverage combined with the benefits of a map including uniform scale and true geometry.
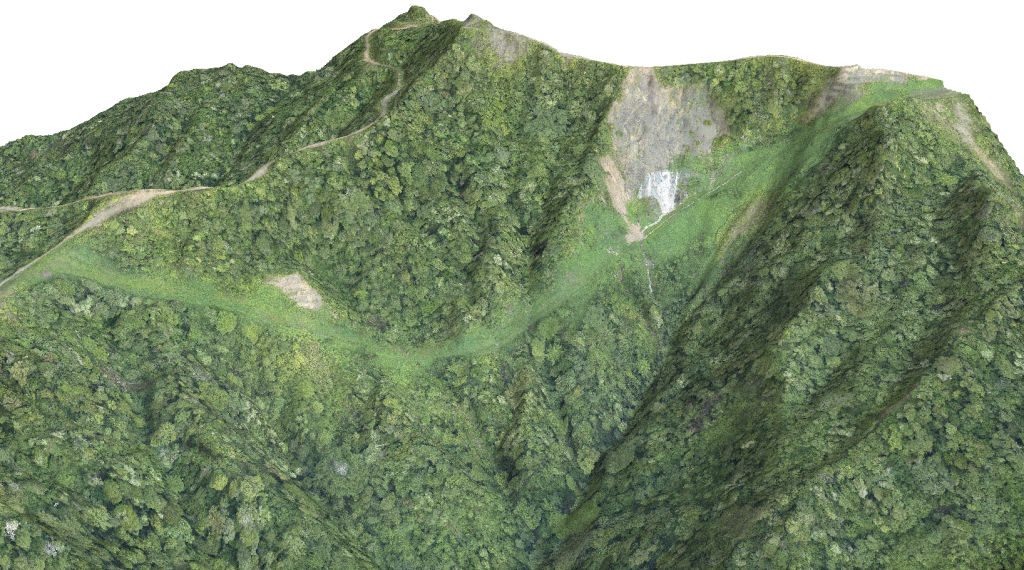
Slope Gradient
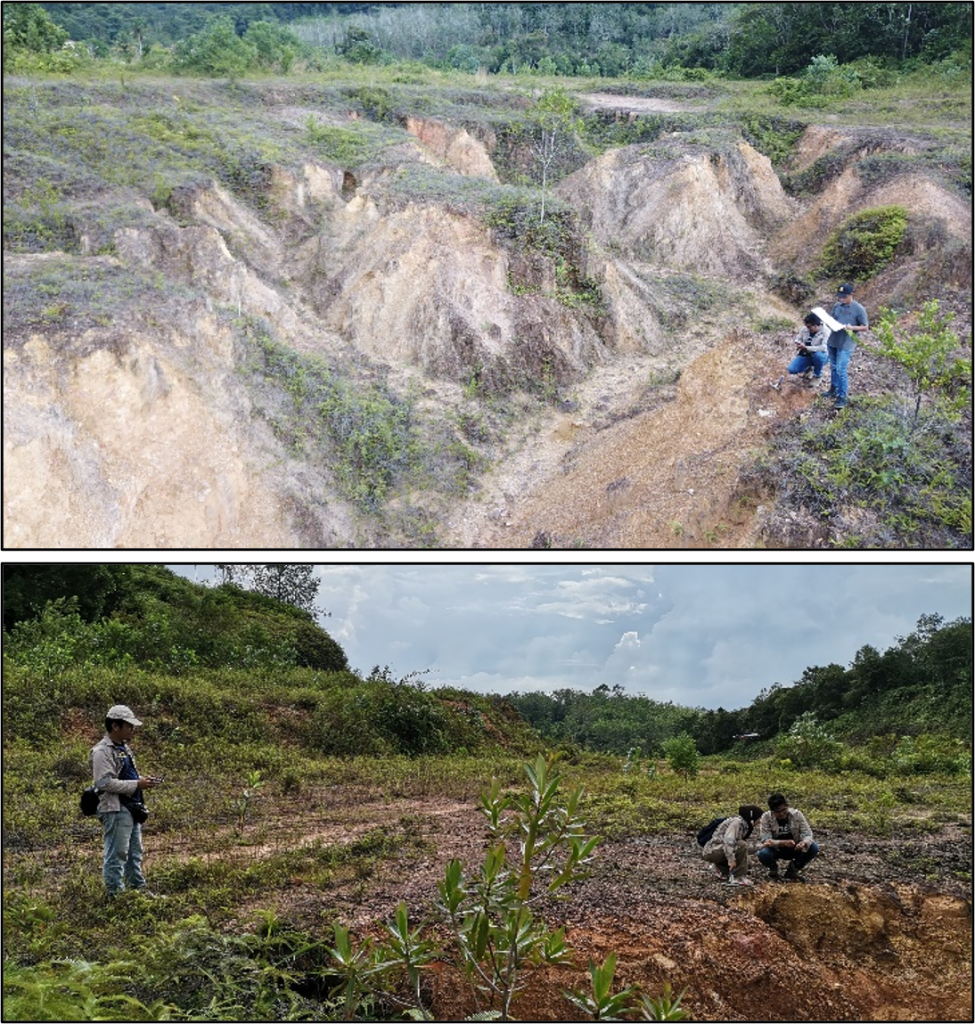
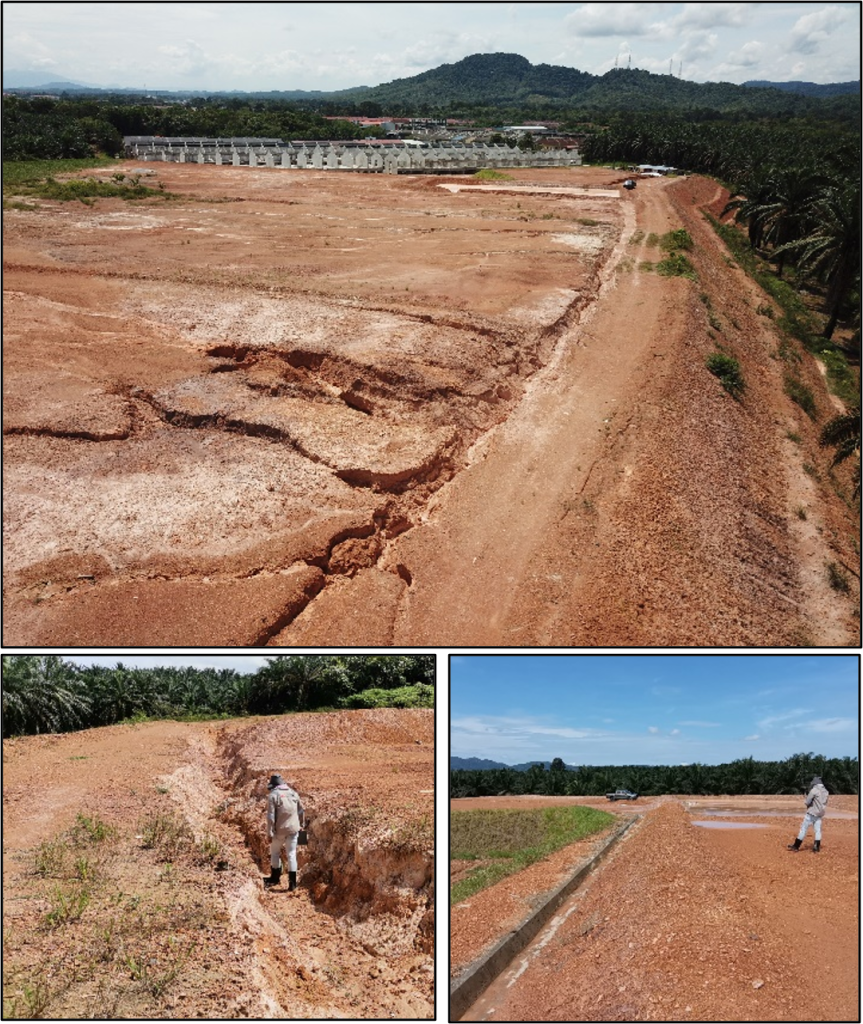
On a slope, the force of gravity can be resolved into two components; a component acting perpendicular to the slope and a component acting tangential to the slope. On a steeper slope, the shear stress or tangential component of gravity increases, and the perpendicular component of gravity decreases. Thus, theoretically steep slopes are likely to cause mass movement compared to gentle slope or flat area. A guideline from government agencies like Minerals and Geosciences Department (JMG) and Department of Town and Regional Planning stated that the degree of risky hilly area starts at 25°. Besides, the hilly area with intrusive acid rock gives higher probability to cause a slope failure (Mukhlisin et al., 2010).
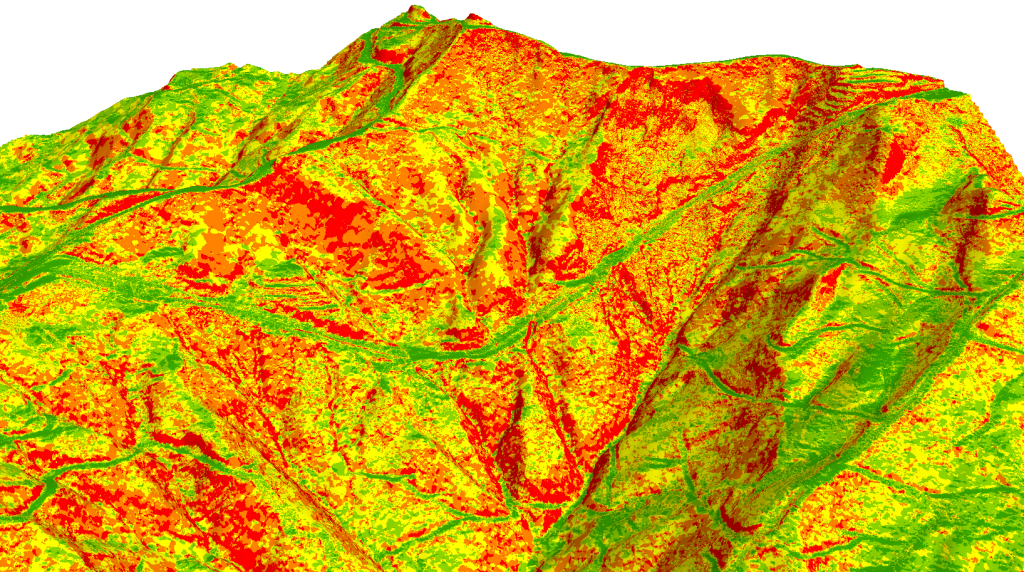
Flow Accumulation
Based on flow direction and topography of slope (gradient and elevation), those areas where water may accumulate during times of intense precipitation can be determined. This is called flow accumulation. Flow accumulation is an indirect way of measuring drainage areas (in raster units) and increases constantly from the drainage divides to the outlet (Schäuble et al., 2008). Flow accumulation is related to water flow from convex and curvature morphology and accumulate at certain area. It is measured based on surface area where water will accumulate which causes soil saturation and resulting in the form of rills, gully and further worse to landslide. Thus, the construction of proper drainage is necessary to carter water away properly. The flow accumulation operation performs a cumulative count of the number of pixels that naturally drain into outlets.
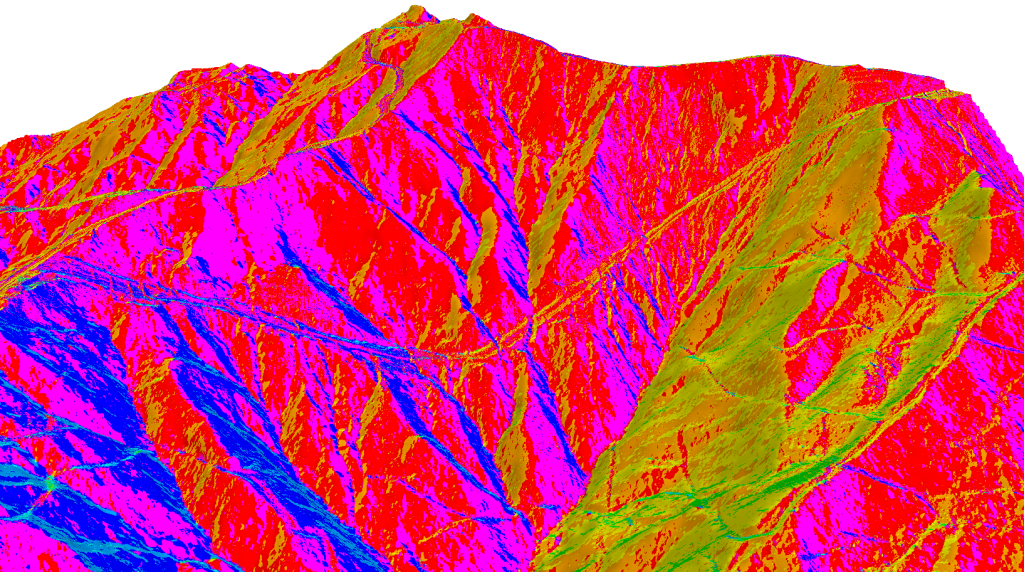
Slope Aspect
Slope aspect indicates the directions of the physical slope’s face. The aspect can be classified based on the slope angle with a descriptive direction. An output aspect raster will typically result in several slope direction classes. In theory, the direction of a slope face with respect to the sun (aspect) has a profound influence on vegetation, erosion and may create microclimate conditions.
Terrain Classification Factor Map
Terrain Classification Map evaluate the component and also the physical appearance of the slope. This is carried out in accordance with JMG’s recommendations. The term used are essentially morphological descriptions and do not necessarily infer the geomorphological processes which are occurring on the slope.
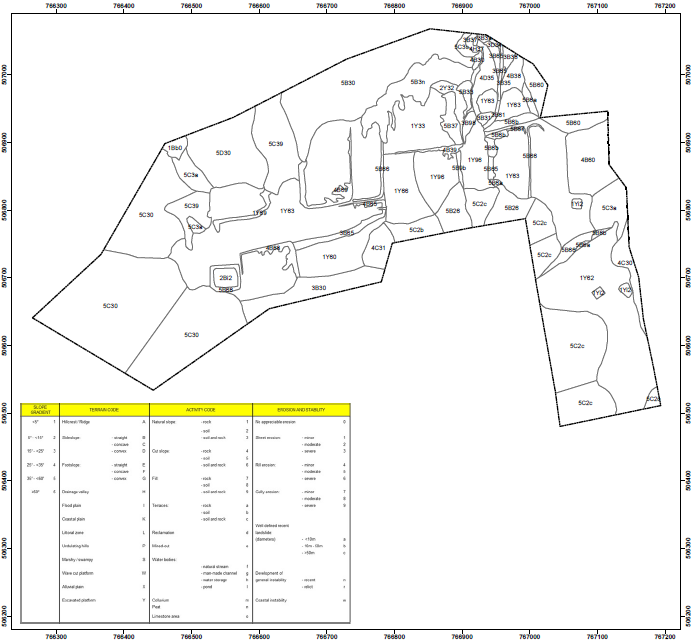
Slope Gradient Factor Map
Slope Gradient Map (SGM) is used as a reference in the field survey and are prepared by using the Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN) or other similar software. This map summarizes
terrain pattern in the map sheet in terms of slope angle. SGM could also be referred to as slope classification map.
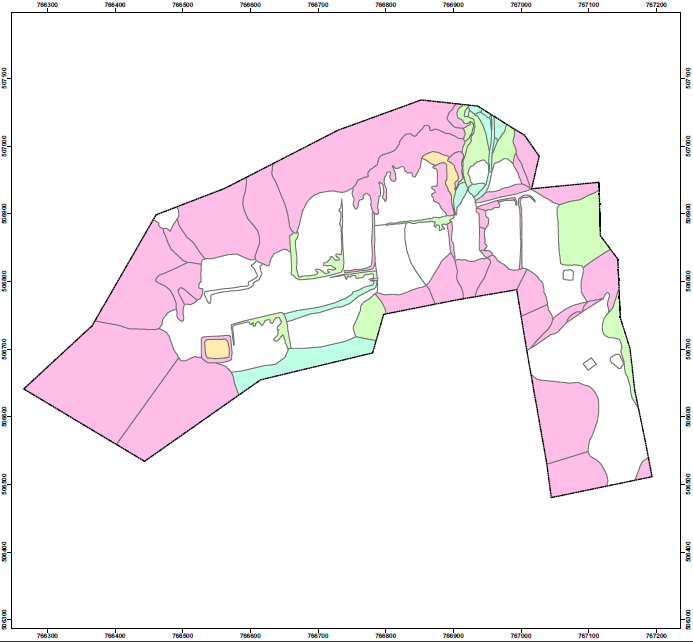
Terrain Component Attributes Factor Map
Terrain Component Attributes Map is an evaluation map of the physical and slope appearances. The slope component attributes of the proposed development are generally characterized as a cut-and-fill platform.
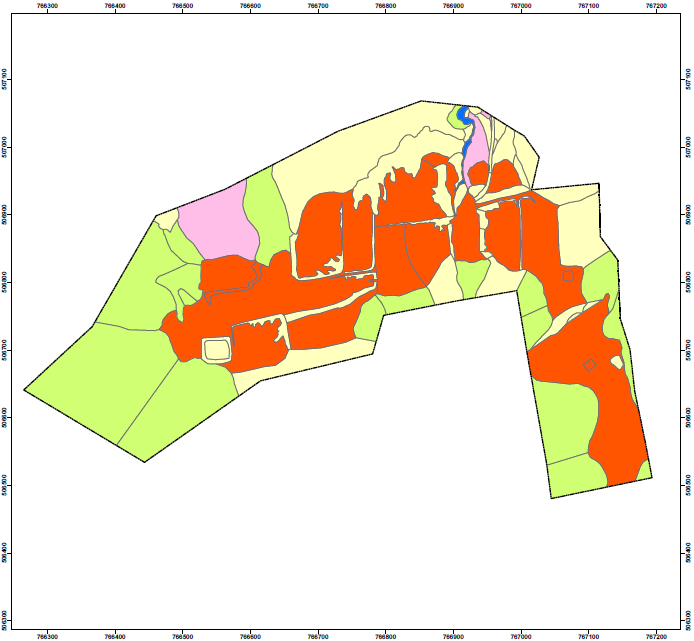
Erosion and Instability Factor Map
The map delineates the broad pattern of erosion and instability and is designed for both technical and non-technical users who may require information regarding the general nature, degree and intensity of erosion and instability for planning and engineering purposes.
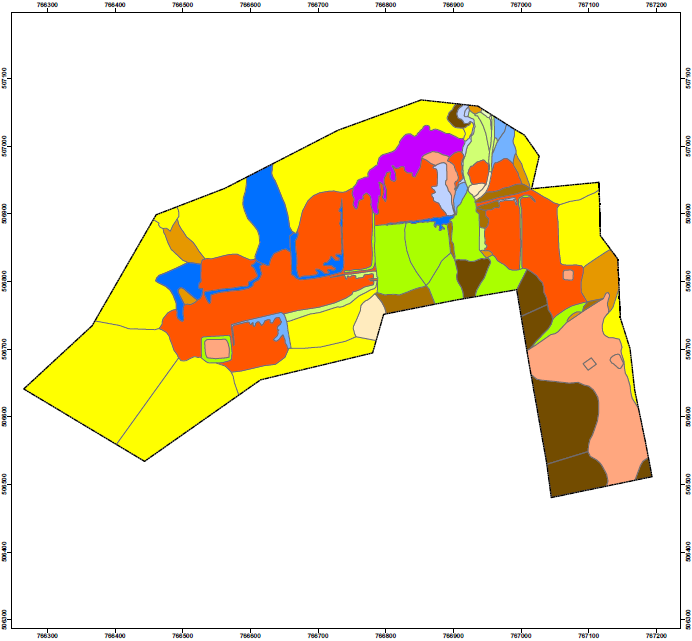
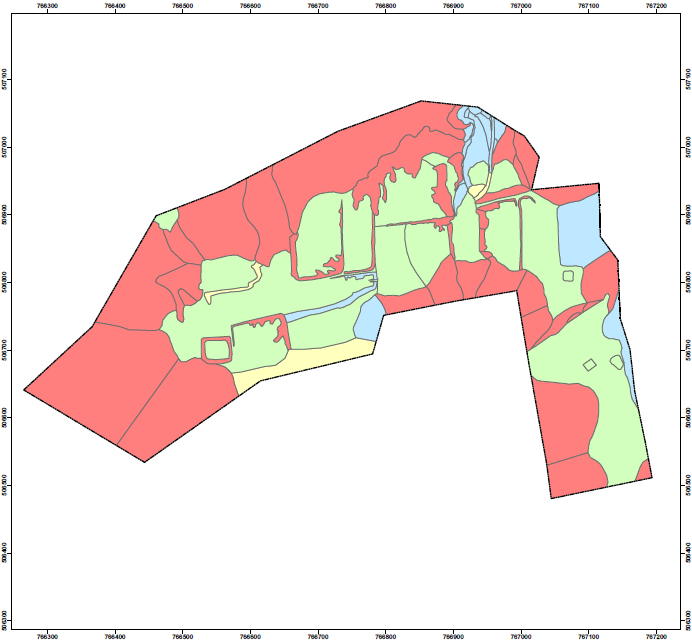
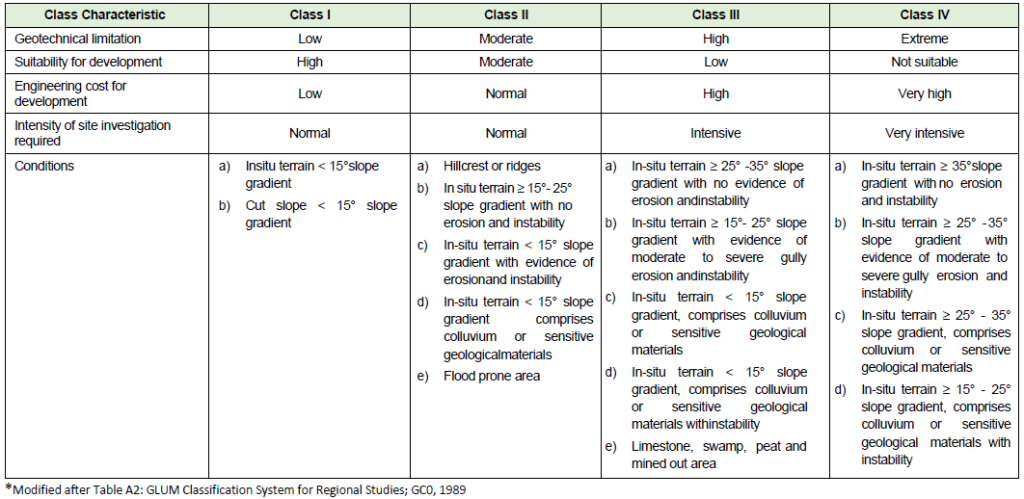
Construction Suitability Map (CSM)
The construction suitability map is the ultimate product of terrain classification map. The suitability classifications are extracted from the JMG (2002) manual JMG GP.06.
For more info:
1. UMK
2. Geotechnica Services



