WHAT IS GIS?
• A geographic information system (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on Earth’s surface.
• GIS can show many different kinds of data on one map, such as streets, buildings, and vegetation.
• This enables people to more easily see, analyze, and understand patterns and relationships.
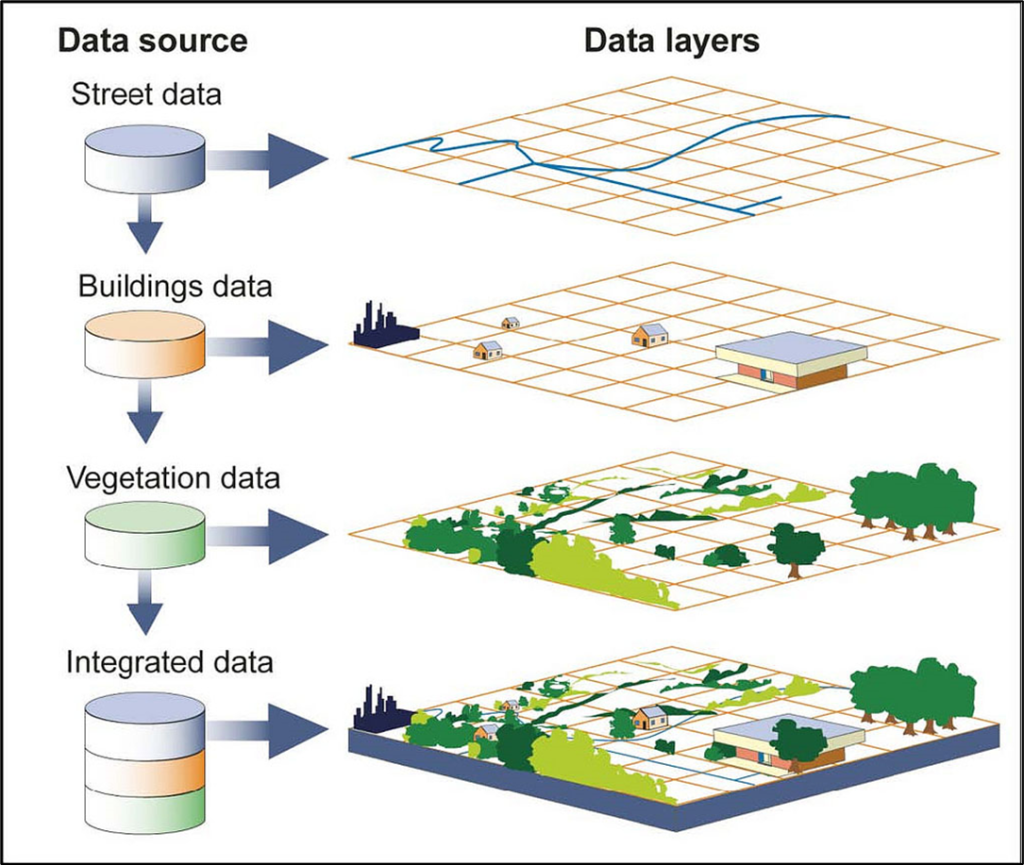
What can SPATIAL DATA do?
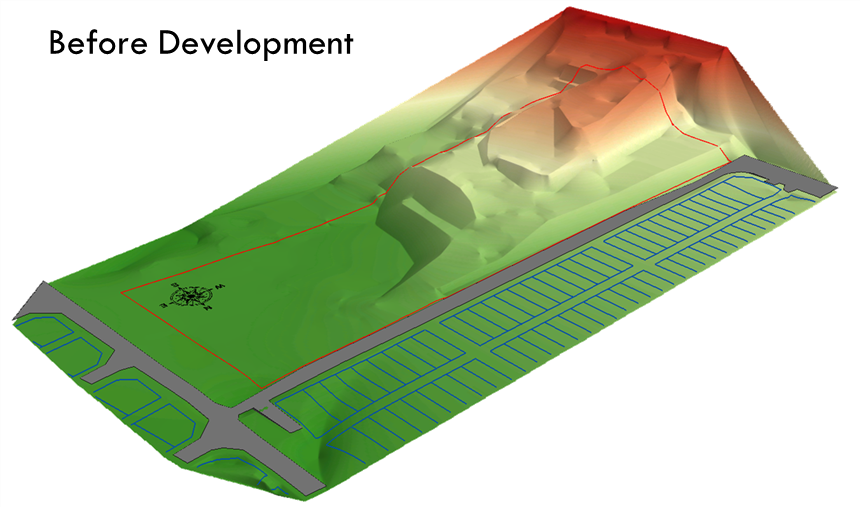
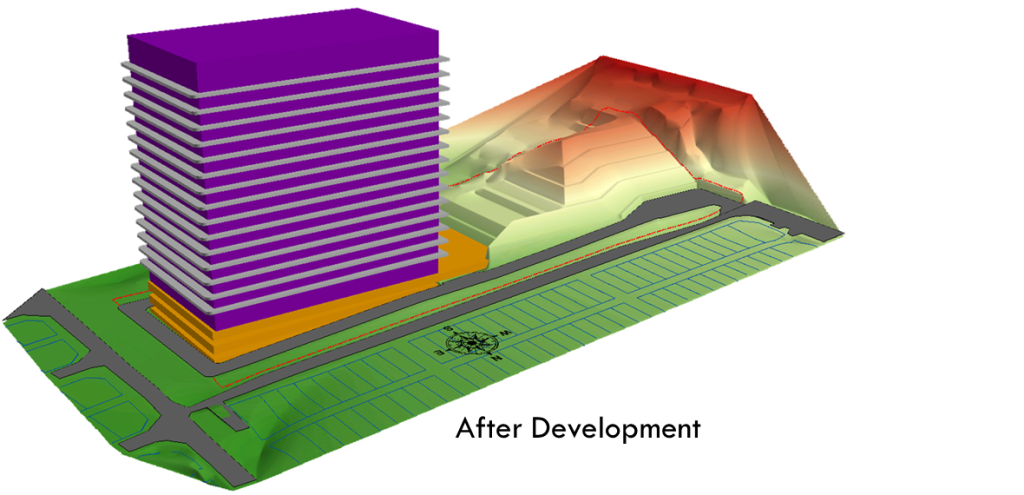
• Spatial data is used in a wide range of applications, including urban planning, natural resource management, environmental monitoring, emergency management, and public health. For example, spatial data can be used to identify terrain for any project of development before and after development.
• It also can showed areas prone to natural disasters, map the spread of diseases, or analyze the impact of land use changes on the environment.
• In each case, spatial data provides critical information that helps decision-makers to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions.
• Spatial data can be collected using various technologies, including GPS (Global Positioning System), LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), aerial photography, and satellite imagery. Once collected, the data can be stored in a spatial database, which allows it to be easily accessed, analyzed, and visualized.

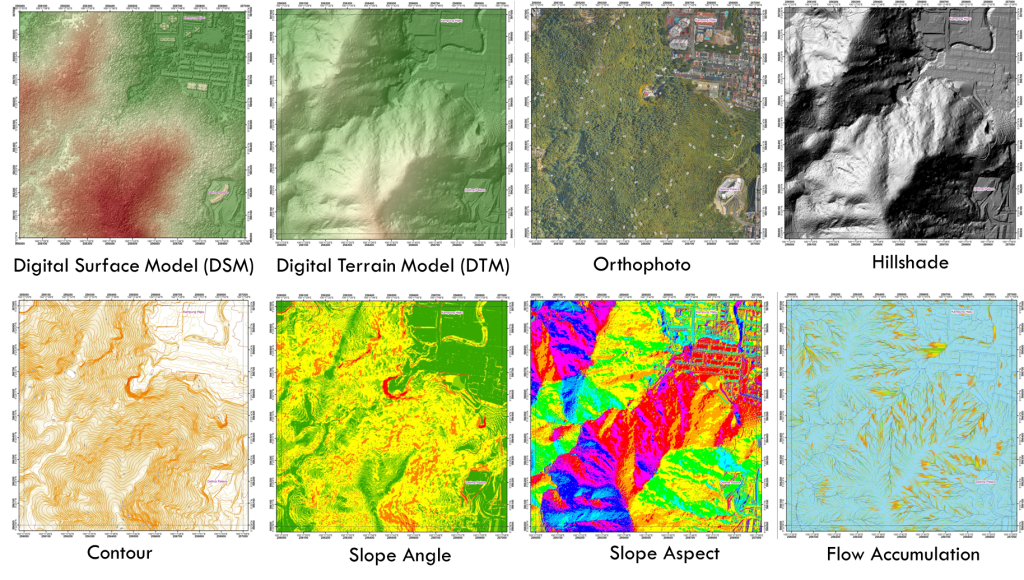
LIDAR DELIVERABLES
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create 3D models of the earth’s surface. LiDAR data can be processed and analyzed to generate various deliverables, including:
•Point cloud: A collection of LiDAR data points that represent the earth’s surface in 3D. Point clouds can be used to create digital elevation models (DEMs) and other visualizations.
•Digital Elevation Model (DEM): A 3D representation of the earth’s surface that shows elevation values at each point. DEMs can be used to create contour lines, slope maps, and other terrain analyses.
•Digital Surface Model (DSM): A 3D representation of the earth’s surface that includes all features such as buildings, vegetation, and other structures. DSMs can be used for land use and land cover mapping and urban planning.
•Canopy Height Model (CHM): A model that shows the height of vegetation or other objects above the ground. CHMs are useful for forest inventory, habitat analysis, and other applications.
•Intensity image: A grayscale image that shows the reflected laser energy. Intensity images can be used for feature extraction, such as building or tree detection.
•3D model: A realistic representation of the earth’s surface that can be used for visualization and simulation purposes.